Depression is a mood disorder that affects how the person thinks, behaves and feels. The feeling of sadness or hopelessness can occur lasting for just a few days, however for some, it can last for years. It is vital to know that depression is different than being upset for a while or disappointed in a particular situation that happens in your day.
While some people can experience minor bouts of depression, others have to deal with severe episodes throughout the rest of their lives. Also known as clinical depression, major depression, or major depressive disorder (MDD), it can interfere with a person’s usual daily activities in work, school, and other social functions. It can significantly affect the person’s relationships as well.
What happens to the mind when you are depressed? For you to be able to be clinically diagnosed with a major depressive disorder, you have to have at least five or more symptoms occur daily over the course of two weeks.
- feelings of extreme sadness and hopelessness

- inappropriate feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- suicide attempt
- recurring thoughts of death or suicide
- difficulty in thought processes such such thinking, making decisions, concentrating
- restlessness and fatigue
- lack of sleep or sleeping too much
- lack of interest in doing activities you once enjoyed doing
- increased or decreased appetite
- weight loss or weight gain
The average age of developing MDD is 32 years old. However, someone at any age can develop this disorder. Experts can’t pinpoint exactly why some people can develop MDD. However, they cite several factors:
- Stress: A stressful event can trigger an episode, such as a divorce or a death of a loved one.
- Genetics: Some people are predisposed to develop this kind of disorder more than others—family history plays a factor.
- Biochemical reactions: The chemicals in the brain for those with MDD is different from a person without the disorder.
- Hormone imbalances: After pregnancy or during menopausal age, there are changes in hormones in a woman’s body causing them to develop MDD.
Depression and the brain
Three parts of the brain can play a vital role in MDD—the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex.
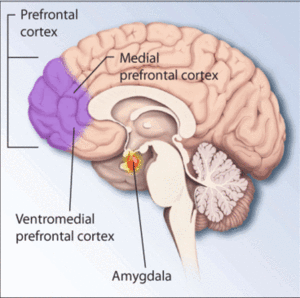 Hippocampus: The hippocampus helps store memories as well as regulates the production of the stress hormone called cortisol. When a stressful situation or hormone imbalance occurs, there is an increased amount of released cortisol. This is harmful in the long run because it impedes the production of new neurons while making the old ones shrink, causing potential memory loss.
Hippocampus: The hippocampus helps store memories as well as regulates the production of the stress hormone called cortisol. When a stressful situation or hormone imbalance occurs, there is an increased amount of released cortisol. This is harmful in the long run because it impedes the production of new neurons while making the old ones shrink, causing potential memory loss. - Amygdala: The amygdala regulates your emotional responses, either it be fear or pleasure. With MDD, the brain is enlarged due to exposure to high levels of cortisol, therefore a disruption of sleep and other activities typically occurs. It also causes abnormal production of hormones and other chemicals that can result in further complications.
- Prefrontal Cortex: The prefrontal cortex regulates hormones, plays a role in decision making and aids the brain in making new memories. Over time, due to increased levels of cortisol, this portion of the brain may shrink as well.
As you can see, cortisol plays a role for people suffering from chronic depression. For a healthy individual, cortisol levels are usually the highest in the mornings and gradually decrease during nighttime. However, with a person with MDD, cortisol levels remain high regardless the time of the day.
Treatment
 Over the years, experts have developed several medications that can help balance out cortisol and other chemicals that cause the brain to shrink. Antidepressant drugs and other medical procedures such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are also prescribed in some cases to alleviate the symptoms.
Over the years, experts have developed several medications that can help balance out cortisol and other chemicals that cause the brain to shrink. Antidepressant drugs and other medical procedures such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) are also prescribed in some cases to alleviate the symptoms.
Simple yet effective tips for helping person prevent or deal with depression
- Eating healthy foods coupled with regular exercise helps that brain stay active as well as keep the body fit. This also stimulates the brain cells while strengthening the links between them. Furthermore, exercise is a natural antidepressant, because it causes your body to release endorphins, also known as your happy hormones, during and following physical activity.
- Having enough sleep helps in repairing brain cells, as well as grow new ones.
- Avoiding taking substances that can potentially destroy brain cells, like illegal drugs and alcohol.
If any of the above sound all too familiar, rest assured that there are many resources available for you. Fortunately, psychotherapy and counselling can have a significant positive impact on the overall psychological health of the patient. That said, if you’re thinking of asking for assistance, Endeavour Wellness can help set you on the pathway to recovery.

Leave a Reply