When someone is diagnosed with diabetes, a doctor will typically recommend that they begin monitoring their blood glucose, or blood sugar, as part of a comprehensive diabetes care plan. Careful tracking of blood sugar levels is important for the safety and health of individuals diagnosed with diabetes, and there are many different methods of monitoring that can be used.
Methods for Testing Blood Glucose Levels
The two most widely-used and effective ways to check blood glucose levels are with a glucometer or a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system. These methods have some key differences:
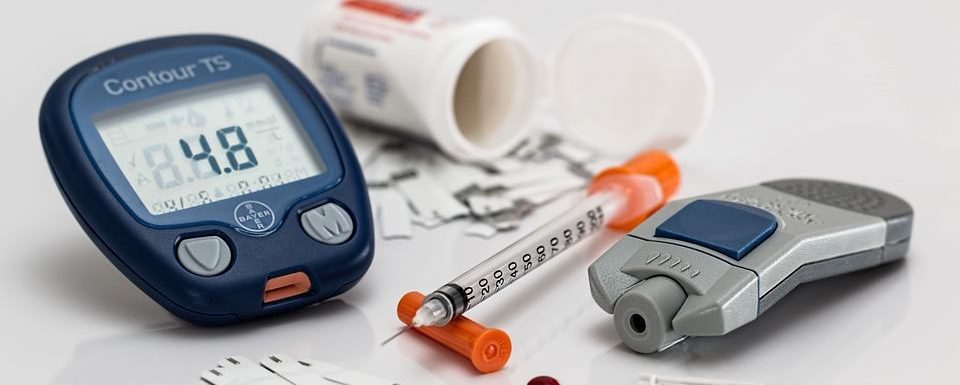
Glucose Monitoring via Glucometer – This method of testing blood sugar levels includes pricking a finger via a small needle to draw a tiny blood sample from the finger. The sample is then placed on a small testing strip that feeds into a blood glucose testing device (glucometer). The glucometer measures and displays the current blood sugar level. Some meters allow patients to test on other parts of the body as well, and they often vary greatly in terms of speed, size, cost, ability to track blood sugar over time, etc.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) System – A continuous glucose monitoring system (CGM) is another method of blood glucose testing. A CGM is a sensor worn at all times that measures the amount of blood glucose just beneath the skin. This method usually requires occasional recalibration with finger prick testing and provides regular information about trends in a patient’s blood glucose levels throughout the day, and over the course of weeks or months. If a patient requires insulin therapy as part of their diabetes care plan, a touchscreen insulin pump with integrated CGM can combine both features into one simple-to-use device.
When to Test Blood Glucose Levels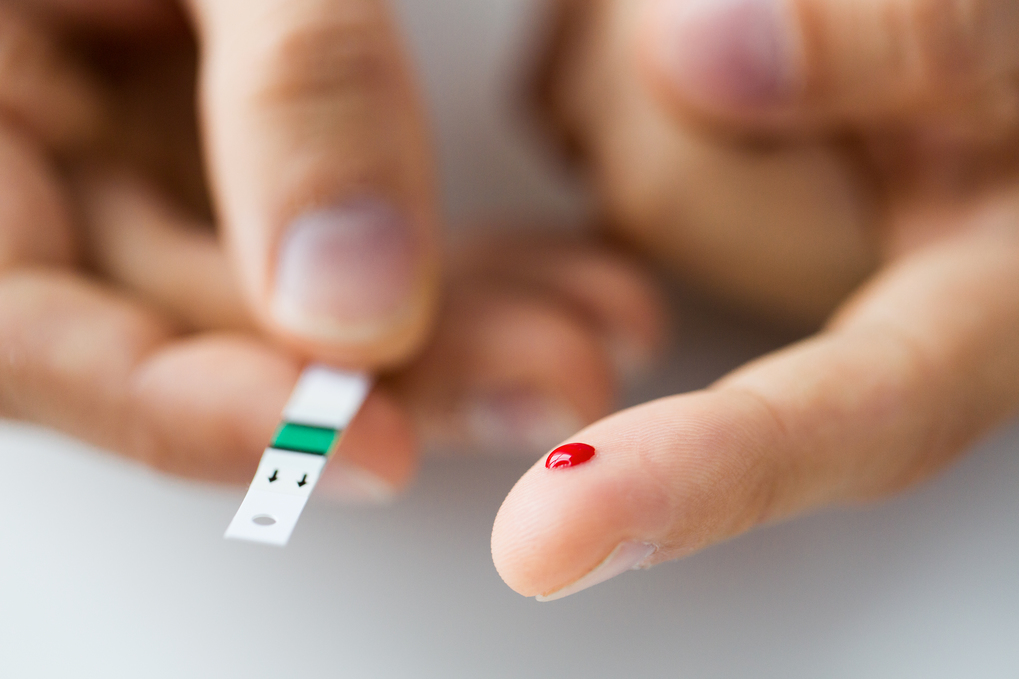
Doctors specializing in diabetes are able to help explain how and when to check blood glucose levels. This can depend of a variety of personal factors, including meals, bedtime, exercise habits, insulin therapy and other medications, and any other illnesses.
Tracking Blood Glucose Levels
Testing blood sugar levels is an important part of avoiding hypoglycemia (episodes of low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (episodes of high blood sugar). It is also important to track the relationship between blood glucose levels and lifestyle habits (diet, exercise, stress etc.) over time. Keeping track of levels can be extremely helpful in drawing conclusions about the effectiveness of a diabetes care plan and how certain activities affect a patient’s blood glucose levels. Some of the common ways to track blood glucose levels are:
Journal – Patients can use a journal to track their daily activities, meals, illnesses, medications, and blood sugar levels. This information can be key to effective diabetes treatment. There are special blood glucose log templates available online for downloading and printing that can be useful for staying organized. If using a physical journal to track blood glucose levels, it is important for patients to remember to bring these records with them to all doctor’s visits.
Online – For some extra guidance, the American Diabetes Association provides a tool called Diabetes 24/7 that can help patients monitor all aspects of their diabetes management plan online and securely send their data directly to their doctor.
Mobile apps – As technology increases, so do the tools that can be used to track health. Using an insulin pump with CGM integrations, blood glucose levels and lifestyle choices can be tracked over time. Through using these tools, patients can allow doctors to have direct access to their blood glucose readings.
Along with their doctors, patients can review blood glucose logs to make important decisions about their diabetes care. If you or a loved one have questions about measuring blood glucose levels or tracking them over time, speak to a doctor who specializes in diabetes for more information.
SOURCES:
https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/home-blood-glucose-testing#1
https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes/top-iphone-android-apps
Leave a Reply